Preparing the Data
Machine Learning Fundamentals with Python
2 min read
Published Nov 16 2025
Guide Sections
Guide Comments
Machine learning starts and ends with data. Before training a model, we need to load, inspect, clean, and prepare the dataset so it’s suitable for algorithms to learn from.
Why Data Preparation Matters
A famous saying in ML:
“Garbage in → garbage out.”
Even the most advanced models will perform poorly if the data is messy, inconsistent, or incorrectly formatted.
Most of your time in real ML projects (often 60–80%) is spent on data preparation and exploration.
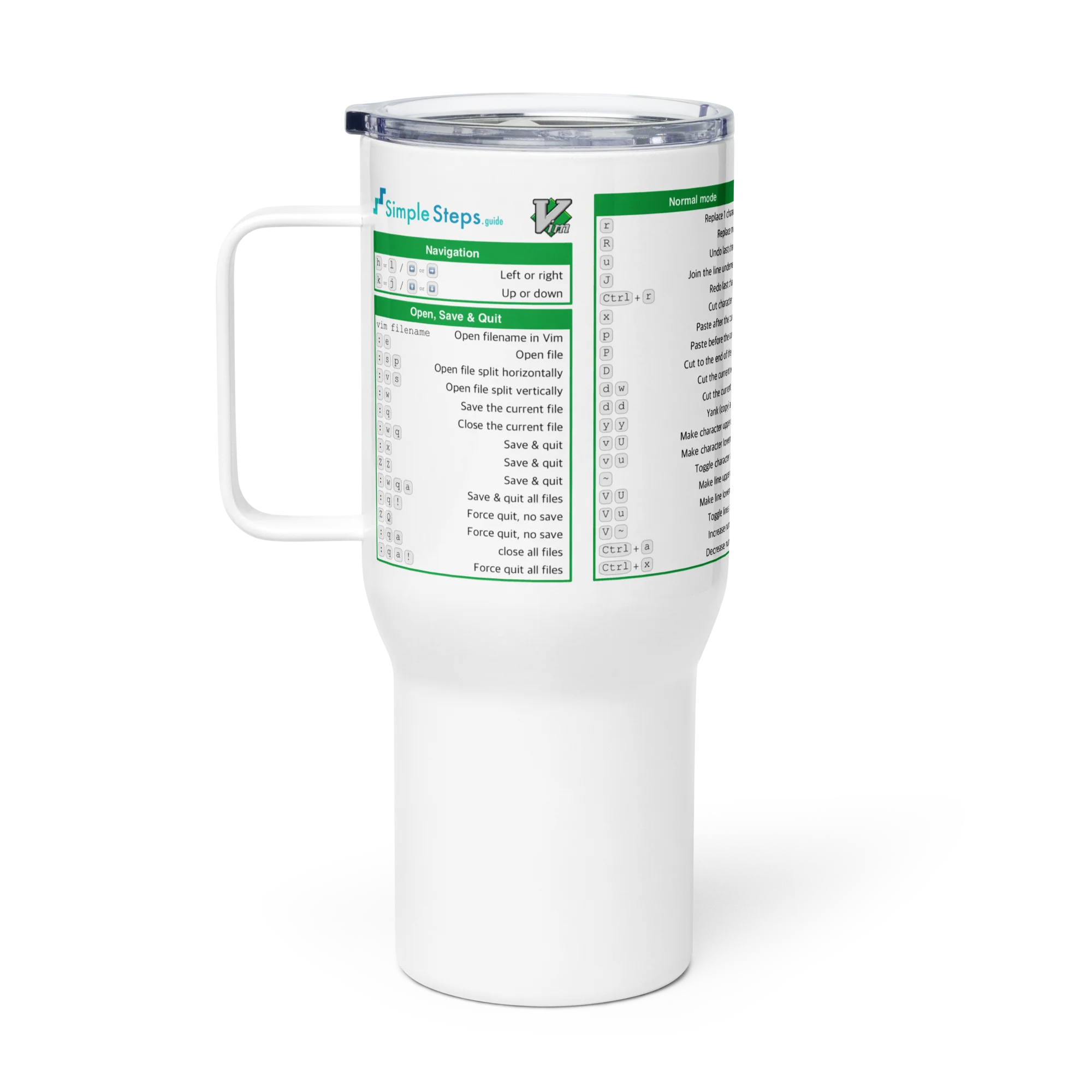
Loading Data
Data can come from CSV files, databases, or APIs.
Example Python code loading the Iris dataset from Seaborn:
Explanation:
.head()shows the first few rows..info()reveals data types and missing values.
Exploring the Data (EDA)
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) helps you understand what’s in your dataset before you model it.
Look at summaries and distributions:
Explanation:
.describe()gives mean, std, min, max, etc.pairplot()helps visualise relationships between features.heatmap()shows how features are correlated (linear relationships).
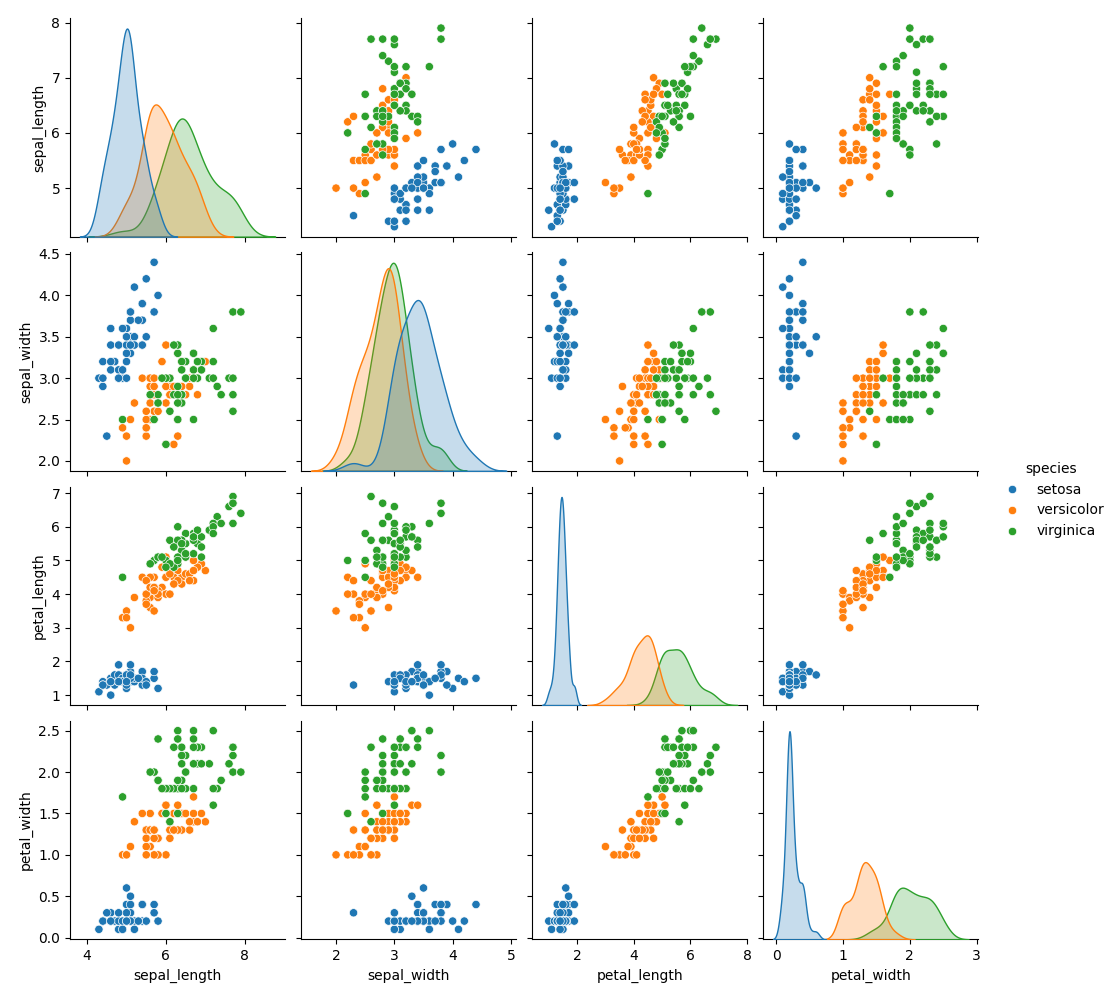
Pairplot of Iris dataset
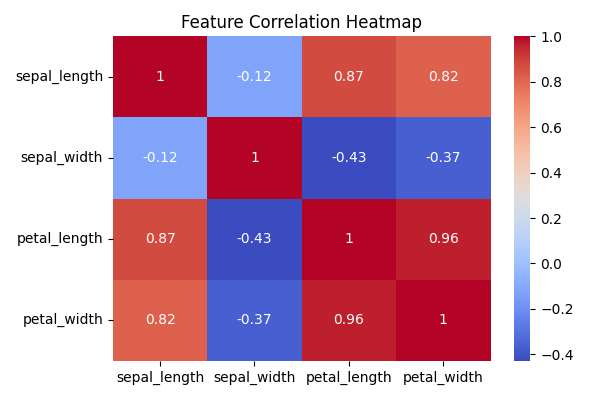
Heatmap of Iris dataset
Handling Missing Data
Datasets often have missing or invalid values. You can either remove or fill them.
Explanation:
dropna()removes missing rows.fillna()replaces missing values (e.g., with mean or median).- Always inspect the effect before choosing a method.
Encoding Categorical Data
Machine learning models work with numbers, not text. We must convert categorical (string) data into numeric form.
Explanation:
LabelEncoderconverts text labels, e.g. "setosa", "versicolor", "virginica" into numeric codes 0, 1, 2.- For non-ordered categories, you can also use one-hot encoding (
pd.get_dummies()):
Feature Scaling
Some algorithms (e.g., K-Means, SVM, Neural Networks) are sensitive to the scale of data. If one feature has much larger values than another, it can dominate the model’s learning.
Two common techniques:
- Standardisation: mean = 0, std = 1
- Normalisation: scales values between 0 and 1
Explanation:
StandardScalercenters and scales to unit variance.MinMaxScalerrescales between 0–1.- Scaling doesn’t change relationships, only value ranges.
Splitting Data into Train and Test Sets
We must train our model on part of the data and test it on unseen data to check generalisation.
Explanation:
train_test_split()randomly divides the dataset.- Typically, 80% training / 20% testing is used.
- The test set simulates unseen data to measure performance objectively.














