Power Law (Pareto) Distribution
Maths: Statistics for machine learning
2 min read
Published Oct 22 2025, updated Oct 23 2025
Guide Sections
Guide Comments
A Power Law Distribution describes a situation where small occurrences are extremely common,
but large occurrences are very rare, following the general rule:
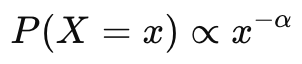
In simple terms:
“A few items account for most of the effect.”
Examples: a few rich people own most wealth, a few websites get most traffic, a few words dominate language use.
It is also known as the Pareto Distribution (after economist Vilfredo Pareto).
Probability Density Function (PDF)

Where:
- xm = minimum possible value (scale parameter)
- α = shape parameter (also called the power law exponent)
The PDF decreases rapidly as x increases — forming a long right tail.
Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF)
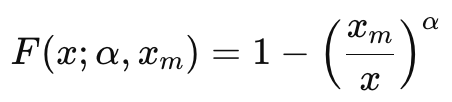
As x → ∞, F(x)→1
Intuition
- Small values are very common (high probability near xm)
- Large values are rare, but not impossible — producing a long tail
- The distribution is scale-invariant, meaning the shape looks the same at any scale:
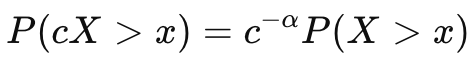
Examples
- Wealth distribution - A few individuals hold most wealth
- Internet traffic - Few sites get most visits
- City populations - Few cities are very large
- Word frequencies - Few words used very often
- Social networks - Few users have many followers
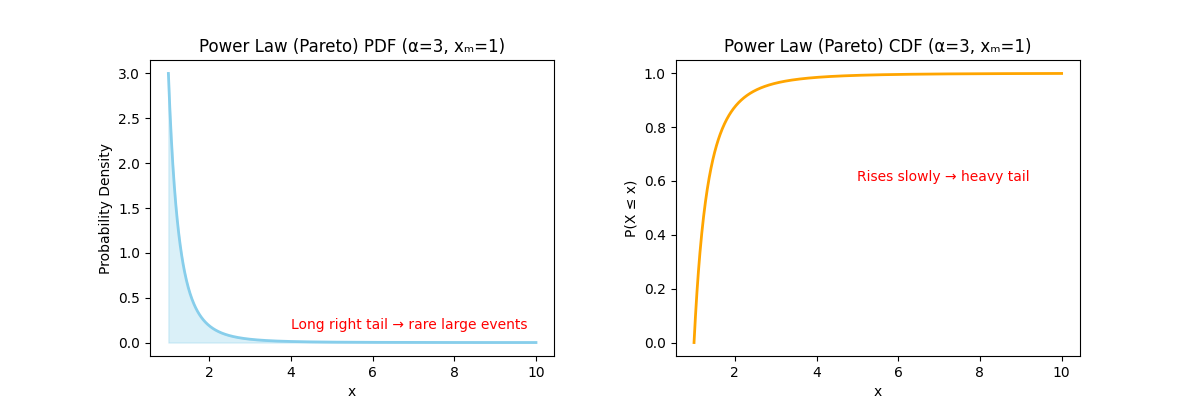
- PDF (left): High probability near the minimum (xₘ), with a long, slow-decaying right tail.
- CDF (right): Increases quickly at first, then slowly approaches 1.
The Power Law shows that extreme events are rare but not negligible.
The tail never fully disappears — there’s always some chance of very large values.
Effect of α (Shape Parameter)
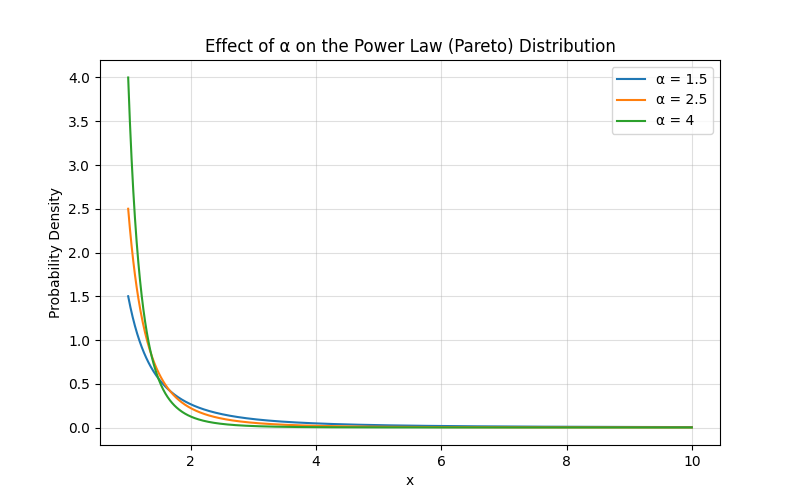
Smaller α → heavier tail (more big events)
Larger α → lighter tail (big events become rarer)
In Machine Learning and Data Science
- Modelling heavy-tailed data - Wealth, web traffic, popularity, network degrees
- Anomaly detection - Detecting rare extreme outliers
- Natural language processing - Word frequencies (Zipf’s law)
- Network science - Power-law degree distributions in social graphs
- Economics / risk modelling - Financial returns, market volatility (tail risk)
- Generative modelling - Sampling realistic “long-tail” distributions














